Carpal Tunnel Syndrome (CTS) is a prevalent and often debilitating condition affecting millions worldwide. It stems from the compression of a crucial nerve in the wrist, leading to a range of symptoms from numbness to pain. This article dives deep into the anatomy, causes, symptoms, and treatments available for CTS, offering a holistic understanding of the condition.
Introduction
Carpal Tunnel Syndrome (CTS) is one of the most commonly diagnosed conditions concerning the hand and wrist. It is characterized by symptoms that arise due to compression of the median nerve, a critical nerve that travels through the wrist’s carpal tunnel. This nerve is essential for sensation in various parts of the hand and for certain motor functions.
Definition of Carpal Tunnel:
Carpal Tunnel Syndrome refers to the medical phenomenon where the median nerve, a primary nerve extending from the forearm into the hand, is pressed or squeezed at the wrist. This compression leads to a variety of symptoms that can impact daily activities and overall quality of life.
Here’s a brief overview of Carpal Tunnel Syndrome:
- Carpal Tunnel Syndrome (CTS) is a condition caused by the compression of the median nerve at the wrist.
- It affects the nerve extending from the forearm to the hand, influencing the sensation in certain fingers.
- This compression can hinder daily activities and decrease quality of life.
Overview of the Carpal Tunnel Structure:
The wrist houses an intricate structure known as the carpal tunnel – a narrow corridor framed by wrist bones on three facets and a firm ligament on the remaining side. Within this conduit, the median nerve and several tendons pass from the forearm into the hand. Given its narrow confines, any inflammation or swelling can easily compress the nerve, leading to CTS.
Causes
Exploring the causes of Carpal Tunnel Syndrome, we find:
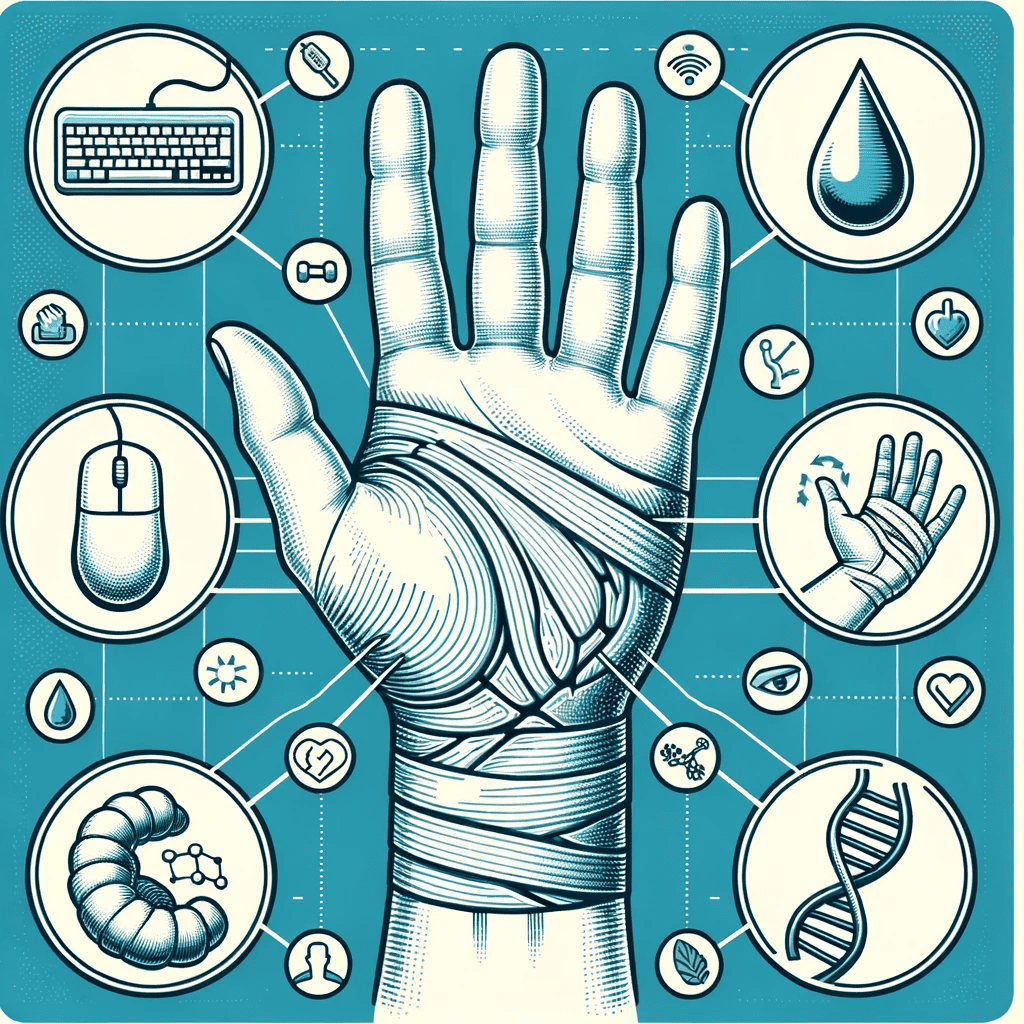
Anatomy of the Wrist and Median Nerve:
Comprised of eight small carpal bones, the wrist is a complex joint. The median nerve, responsible for sensation in the thumb and first three fingers, navigates its way through these bones, making it susceptible to compression if there’s any misalignment or inflammation.
Repetitive Wrist Movements:
Many modern-day activities, from computer work to assembly line tasks, involve repetitive wrist actions. Over time, these constant movements can cause inflammation and swelling in the wrist region, predisposing individuals to CTS.
Wrist Injuries:
A direct injury, like a fracture, can lead to acute swelling in the wrist. This sudden inflammation can exert pressure on the median nerve, triggering the onset of CTS symptoms.
Rheumatoid Arthritis and Other Inflammatory Conditions:
Chronic inflammatory conditions, such as rheumatoid arthritis, can cause inflammation of the joints and tissues. In the wrist, this persistent inflammation can lead to nerve compression, manifesting as CTS.
Pregnancy and Fluid Retention:
Pregnancy often brings about hormonal changes, leading to fluid retention. This can cause swelling in various parts of the body, including the wrists, thereby compressing the median nerve.
Other Contributing Factors:
While the aforementioned factors are primary contributors, other conditions like diabetes, hypothyroidism, or even wrist cysts can elevate the risk of developing CTS.
Symptoms
Anatomy of the Wrist and Median Nerve:
The wrist is an engineering marvel, consisting of eight carpal bones intricately arranged in two rows. This design, while efficient for movement, can be a potential problem for the median nerve. As this nerve weaves its way through the carpal bones, even minor misalignments or inflammation can cause compression, leading to CTS.
Repetitive Wrist Movements:
Our modern world, whether it’s about swiping on touchscreens or typing away at keyboards, demands constant wrist action. Activities, when repeated day in and out, can lead to tiny inflammations in the wrist. This inflammation, while seemingly minor, can add up over time, predisposing the wrist to CTS. Hence, office workers, artists, and even gamers can find themselves at risk.
Wrist Injuries:
Injuries, especially those involving the wrist, can be the starting point for many complications. A fracture, for instance, can cause acute swelling. This abrupt inflammation in a space-limited region like the wrist can put immense pressure on the median nerve, rapidly bringing about CTS symptoms.
Rheumatoid Arthritis and Other Inflammatory Conditions:
Inflammation is a primary concern for the wrist. Chronic conditions like rheumatoid arthritis, characterized by persistent inflammation, pose a significant risk for CTS. The continuous swelling and inflammation can easily compress the already vulnerable median nerve.
Pregnancy and Fluid Retention:
Pregnancy is a beautiful phase, but it’s also a period of profound bodily changes. The hormonal shifts can lead to fluid retention. While this is a natural part of pregnancy, the resultant swelling, especially in the wrists, can compress the median nerve, leading to CTS. This is why some pregnant women experience tingling or numbness in their hands.
Other Contributing Factors:
While direct causes are often emphasized, underlying conditions can play a silent yet significant role. For example, diabetes can cause nerve damage, making nerves more susceptible to compression. Similarly, conditions like hypothyroidism can cause generalized swelling, including in the wrist, thus elevating the risk of CTS.
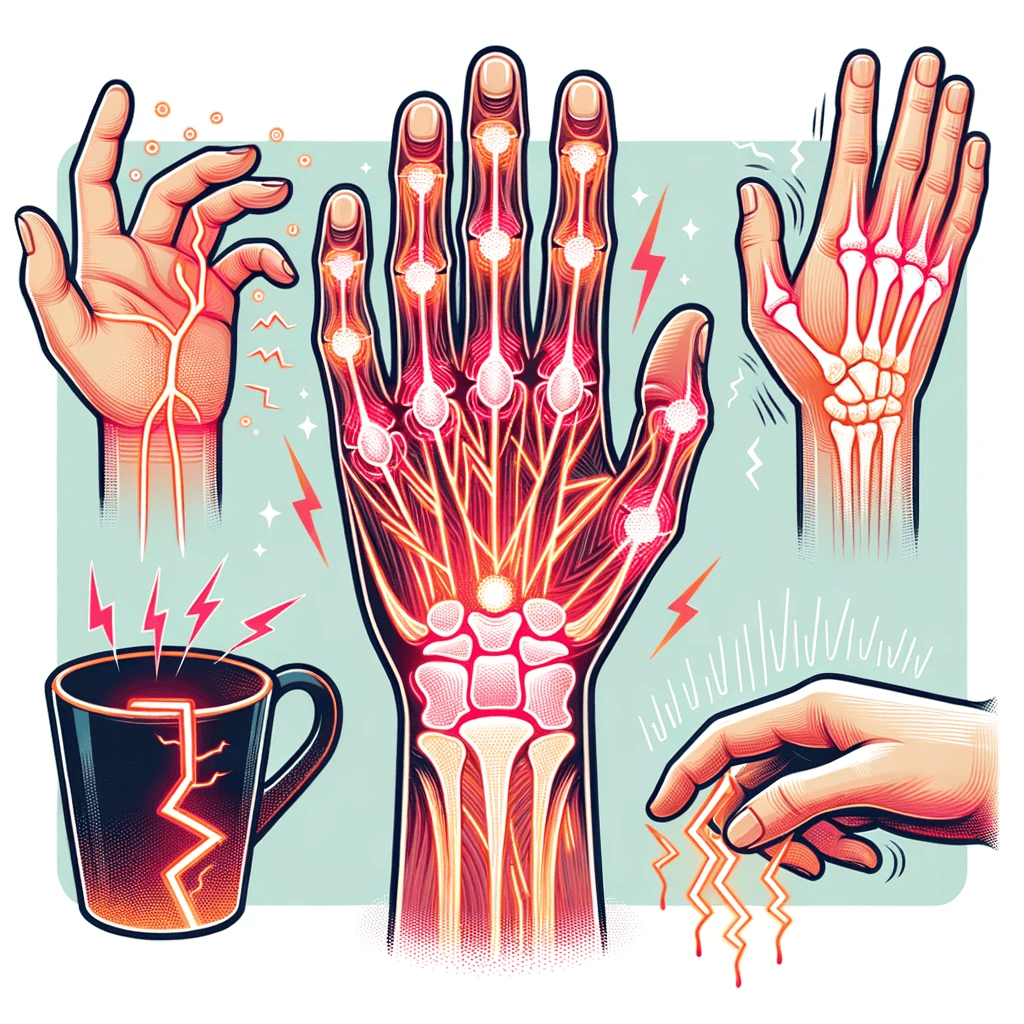
The manifestation of CTS can vary, but common symptoms include:
- Numbness and Tingling: Often the initial symptoms, individuals may experience these sensations predominantly in the thumb, index, and middle fingers.
- Weakness in the Hand: Over time, the compression might lead to a decrease in grip strength, making it challenging to hold onto objects.
- Pain Radiating Up the Arm: Some people report a shooting pain that travels from the wrist upwards, sometimes reaching as far as the shoulder.
- Nighttime Symptoms: Interestingly, many individuals with CTS report exacerbated symptoms at night, often leading to disrupted sleep.
Risk Factors
Understanding the risk factors can help in early diagnosis and management:
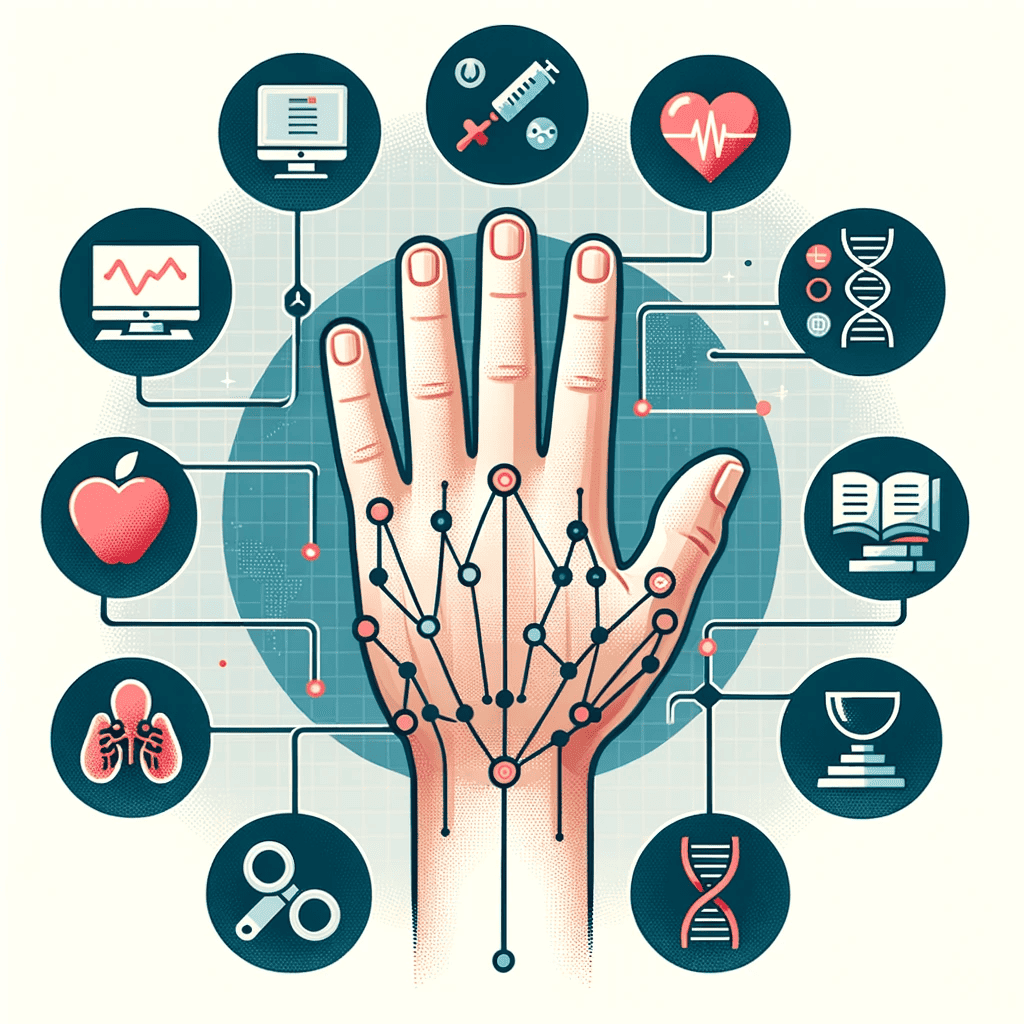
- Occupation and Repetitive Tasks: Jobs that involve frequent wrist motion, like typing or assembly line work, pose a higher risk.
- Gender: Statistically, women are more prone to CTS, possibly due to having smaller carpal tunnels.
- Health Conditions: Conditions like diabetes or thyroid disorders can make one more susceptible.
- Lifestyle Factors: Habits like smoking can reduce blood flow, increasing the risk of nerve damage.
Diagnosis
Diagnosing CTS is a blend of physical examinations, patient history, and specialized tests. Accurate diagnosis is crucial for effective management:
Physical Examination:
The first step usually involves a detailed wrist examination. A trained physician looks for signs of swelling, tenderness, or any deformities. Tapping the wrist, a maneuver known as Tinel’s sign, can sometimes elicit the tingling sensation typical of CTS.
Nerve Conduction Studies: This diagnostic tool is crucial in assessing the median nerve’s health. It measures how fast electrical impulses travel through the nerve. A delay or blockage in these signals can indicate compression or damage.
Electromyogram (EMG): Muscles produce tiny electrical discharges when activated. An EMG records these discharges, providing insights into the health of muscles and the nerves activating them. If there’s a delay or abnormal pattern, it can indicate a nerve issue, such as CTS.
X-rays or MRI: While CTS itself won’t show up on an X-ray or MRI, these imaging modalities are essential when other conditions, like fractures or arthritis, need ruling out. They provide a detailed look at the wrist’s anatomy, helping clinicians determine if there are other underlying issues.
Treatment
There’s a range of treatments, from conservative to surgical:
Non-surgical Treatments: Initial stages of CTS can often be managed without surgery. Wrist splints, especially worn at night, can help maintain the wrist in a neutral position, relieving pressure on the median nerve. NSAIDs, like ibuprofen, can alleviate inflammation and pain. Corticosteroid injections into the wrist can also offer temporary relief by reducing swelling.
Surgical Treatments: In severe cases, when non-surgical methods fail to provide relief, surgery might be the next step. The most common surgical procedure is called carpal tunnel release. It involves cutting the ligament around the wrist to reduce pressure on the median nerve. The procedure has a high success rate, but like all surgeries, it comes with potential risks and a recovery period.
Alternative Therapies: While mainstream treatments are widely recommended, some individuals find relief with alternative therapies. Acupuncture has shown potential in alleviating CTS symptoms. Similarly, chiropractic care, focusing on the hand and wrist, might relieve symptoms.
Prevention
Prevention is always better than cure:
Prevention is the cornerstone of health, and the same applies to CTS.
Ergonomic Adjustments: Ensuring a proper workstation setup can go a long way in preventing CTS. Keyboards should be at elbow height, and wrists should be in a neutral position while typing. Ergonomic accessories, like wrist rests, can also help.
Regular Breaks and Exercises: Taking regular breaks, especially during tasks that strain the wrist, is essential. Simple wrist stretches and exercises can help maintain flexibility and strength, reducing the risk of CTS.
Maintaining a Healthy Weight: Obesity can be a risk factor for many conditions, including CTS. The excess weight can cause generalized inflammation, which can, in turn, affect the wrist. Hence, maintaining a healthy weight through diet and exercise is crucial.
Treating Underlying Conditions: Managing and treating conditions like diabetes, rheumatoid arthritis, or hypothyroidism can indirectly prevent the onset of CTS. Regular check-ups and adherence to medications can help in this aspect.
Complications
If left untreated, CTS can lead to:
Permanent Nerve Damage: Persistent compression of the median nerve can lead to irreversible damage. This means that even if the compression is later relieved, the nerve might not fully recover, leading to persistent symptoms.
Loss of Hand Function: The hand’s intricate functions, from gripping to fine movements, rely heavily on the median nerve. Prolonged CTS can diminish these functions, severely impacting daily activities.
Recurrence: Successfully treating CTS doesn’t render one immune. If the risk factors, like repetitive wrist movements or underlying conditions, remain unaddressed, CTS can make a comeback.
Conclusion
In conclusion, Carpal Tunnel Syndrome, while common, is a condition that requires understanding, early detection, and proactive management. Whether you’re at risk, showing early signs, or know someone affected, being informed is the first step towards a pain-free life.

